Within its multifaceted initiatives, GDS has embraced Climate Resilience as both a core and cross-cutting theme. This strategic approach manifests in two dimensions: dedicated projects aimed at building climate resilience and the infusion of climate resilience activities into existing projects. The approach GDS adopts is comprehensive, encompassing various strategies that synergize to create an integrated response to climate resilience challenges:
- Integrated Land and Water Management: A cornerstone of GDS’s approach is channelling efforts through MGNREGA to manage land and water resources effectively. This includes the implementation of infrastructural projects that mitigate climate-related vulnerabilities.
- Climate-Resilient Agricultural Practices: GDS promotes the adoption of climate-resilient agricultural practices, empowering farmers to navigate the changing climate landscape. This encompasses techniques like soil conservation, crop diversification, and efficient water management.
- Tailored Agro-Meteorological Advisories: Leveraging technology, GDS provides farmers with customized agro-meteorological advisories. These advisories optimize input usage and enhance agricultural productivity, aligning with climate-resilient practices.
- Program Convergence: GDS facilitates convergence with complementary programs such as State Rural Livelihood Mission (SRLM), agriculture, horticulture, and forestry initiatives. This coordinated effort maximizes the impact of climate resilience interventions.
- Skill Enhancement for Income Generation: GDS recognizes skill development as a catalyst for income generation. The organization offers training to upgrade skills, enabling individuals to enhance their livelihoods and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
- Empowering Community Groups: Collaboration with farmer groups and Women Self-Help Groups (SHGs) serves as a potent mechanism to propagate climate resilience practices at the grassroots level.
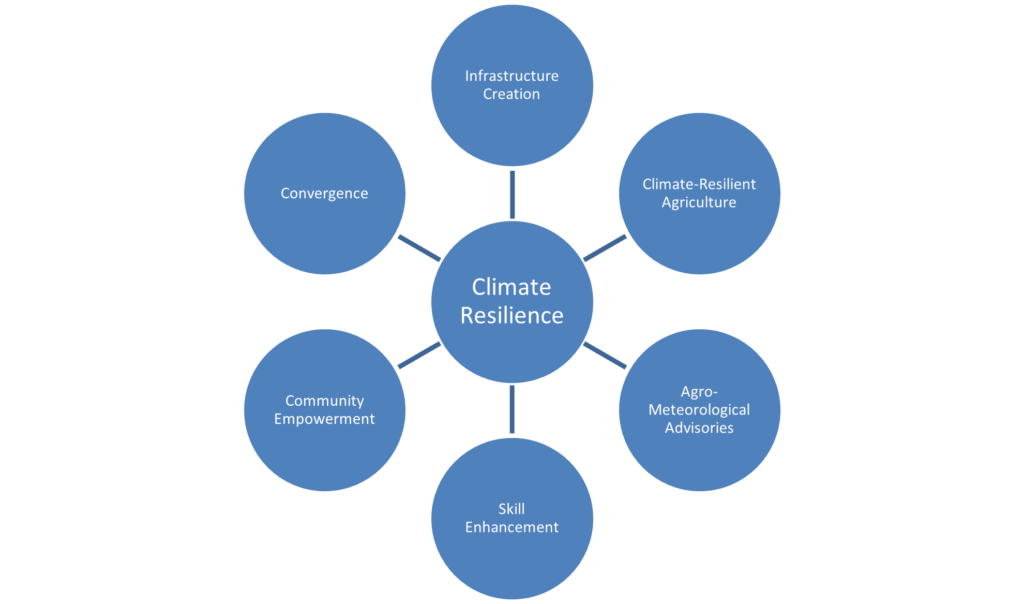
The central tenet of GDS’s strategy lies in convergence, a focused alignment of efforts that enhances infrastructure productivity, fortifies livelihoods, improves resilience, and fosters rural economic growth. By synergizing interventions, GDS ensures that climate resilience permeates the fabric of its projects, safeguarding communities and empowering them to thrive amidst evolving climatic challenges. This holistic approach, illustrated below, embodies GDS’s commitment to a sustainable and resilient future.
A testament to this commitment is the project “Infrastructure for Climate Resilient Growth”, undertaken at the Ajmer (Rajasthan) location in 2022-23, in collaboration with UNDP. The project’s overarching aim was to bolster the resilience of rural communities by fostering convergence and scalability of livelihood options intertwined with rural infrastructure development schemes, particularly the Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS). The project had three l objectives: first, to augment the livelihood security of vulnerable rural populations, especially those with constrained adaptive capacities; second, to enhance the productivity of infrastructural assets established through MGNREGS; and, third, to fortify the resilience of impoverished communities while concurrently supporting the growth of the rural economy. The key interventions under the project were as below:
Capacity Building for Climate Resilience: Empowering Communities for Action
GDS’s commitment to building climate resilience is epitomized by its comprehensive capacity-building initiatives, spanning a spectrum of stakeholders from community members to local governance bodies. These programs are strategically designed to enhance awareness, instill skills, and drive proactive responses to climate challenges. Through a series of focused activities, GDS aims to strengthen the adaptive capacities of communities and institutions alike. For community level capacity building, the modules were on water and soil conservation, climate-smart farming, and rooftop rainwater harvesting system and covered 2847 participants through 85 training events. A training programme designed for MNREGS mates, was delivered through11 batches (439 participants) for enhancing their understanding of tasks and technical aspects of constructing climate resilient infrastructure.
Also, two trainings were organized for 63 ‘Community Climate Managers’, for disseminating climate advisories generated from Automated Weather Stations. Agro-advisory services were extended to over 2000 farmers via platforms like Secufarm. Similarly, for climate-smart GPDP preparation, GDS supported the gram panchayats, in developing detailed project reports for 31 NRM projects.
Converging for Impact
GDS facilitated convergence with MNREGA and various line departments to channel benefits to communities. Through collaborative efforts, 31 detailed project reports (DPRs) were prepared, addressing crucial needs. 68 applications for goat sheds were submitted, with 09 sanctioned. Promotion of climate-resilient agricultural practices saw 198 farmers receiving seeds, and 16 adopting super composting methods. Convergence with PHED led to the treatment of 8 lakh liters of water, benefiting 178 members.
Promoting Climate-Smart Agriculture
the strategy for promotion of climate-smart agriculture focused at crop diversification, irrigation management, and organic cultivation. Transformative changes include replacing maize with Bajra and wheat with Barley, alongside promoting efficient fodder cultivation practices. Through community mobilization, 65 farmers adopted fodder chopping, minimizing wastage.
Promoting Nutrition Gardens
GDS introduces kitchen gardens to enhance nutrition levels among women and adolescent girls while managing grey water sustainably. Orientations and training sessions resulted in establishment of 223 backyard kitchen gardens. Women SHG federations provided seeds, and ICRG team extended technical support, translating into tangible improvements in household nutrition.
Enhancing Social Security Access
GDS facilitates community meetings, orientations, and application camps to expedite access to social protection schemes. Over 328 applications were submitted across various schemes, aiding labor and education departments. GDS’s proactive approach also ensures access to left-out beneficiaries, amplifying the reach of health guarantee schemes.
Weather Stations for Informed Farming
The installation of 02 Automated Weather Stations (AWS) in Taragarh and Badakheda Gram Panchayats supports over 2000 farmers with real-time weather updates through the Secufarm mobile app. Tailoring agro-advisories for maize in Kharif and wheat in Rabi seasons maximizes agricultural efficiency.
Sharing Experiences and Learnings
GDS organized knowledge sharing through a district-level roundtable workshop. This gathering, which drew participation from practitioners, government officials, and CSO partners facilitated an exchange of insights. Diverse perspectives, ranging from GDS’s interventions to successful climate smart practices, enriched the dialogue.
